Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of Pension Plans
- Navigating Different Types of Pensions
- The Importance of Contributions and Employer Roles
- Maximizing Your Pension Benefits for Retirement
- Common Misconceptions About Pensions and Retirement Planning
- Q&A
- Concluding Remarks

Understanding the Basics of Pension Plans
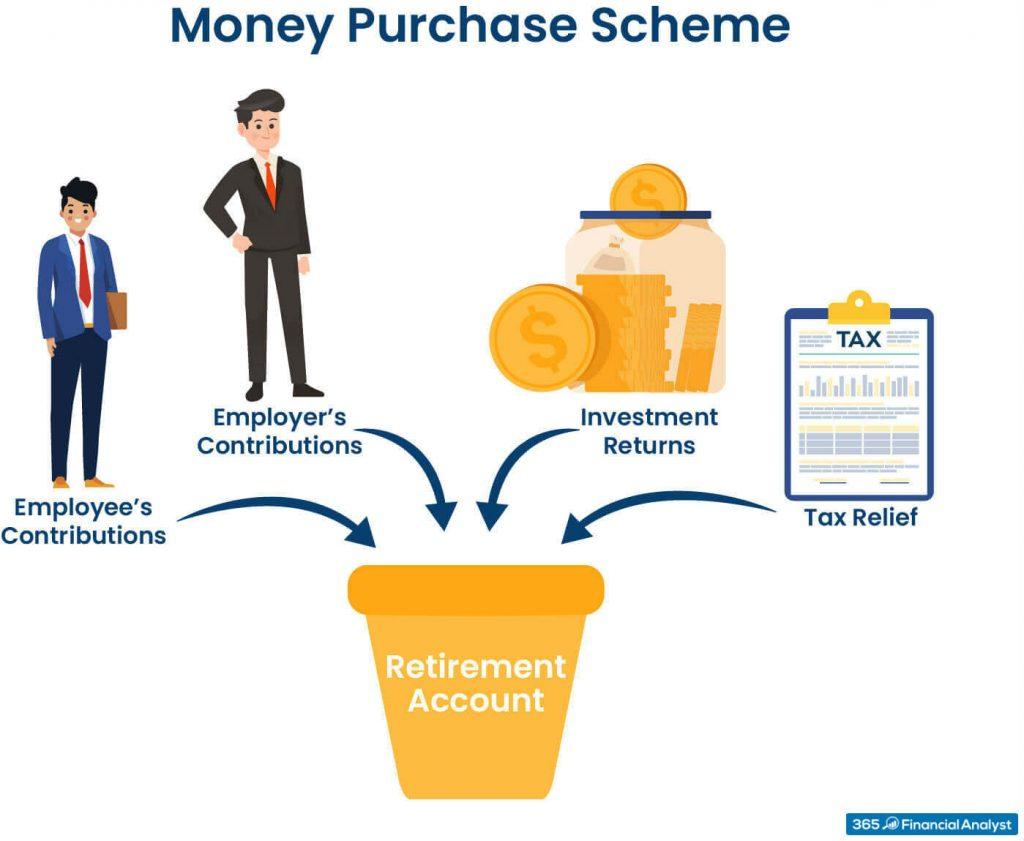
Pension plans are essential financial tools designed to provide individuals with income during retirement. Understanding the various types of pension plans is crucial for making informed decisions about your future. There are generally two main categories of pension plans: defined benefit plans and defined contribution plans. Defined benefit plans promise a specific payout during retirement, determined by factors such as salary history and duration of employment. In contrast, defined contribution plans rely on contributions made by both the employer and employee, along with investment performance, to determine the retirement payout.
When considering a pension plan, it’s important to evaluate several key aspects:
- Employer Contributions: Understand how much your employer contributes to your plan, as this can significantly affect your retirement savings.
- Vesting Period: Be aware of the vesting schedule, which dictates how long you must work for your employer before you retain their contributions.
- Withdrawal Options: Familiarize yourself with the options available for withdrawing funds upon retirement, as well as any penalties for early withdrawal.
The following table summarizes the main differences between the two primary types of pension plans:
| Feature | Defined Benefit Plans | Defined Contribution Plans |
|---|---|---|
| Benefit Structure | Fixed monthly payment | Variable payment based on contributions and investments |
| Investment Risk | Employer bears the risk | Employee bears the risk |
| Management | Managed by the employer | Managed by the employee |
Understanding these fundamental principles of pension plans can greatly aid in planning a secure and comfortable retirement. It’s essential to assess both personal financial goals and career paths while navigating the complexities of pension options, ensuring that you select a plan that aligns with your future aspirations in retirement.


Navigating Different Types of Pensions
Understanding the landscape of pensions is essential for planning a secure financial future. There are primarily three types of pensions, each designed to cater to different circumstances and retirement planning needs. These include defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans, and state pensions, each having distinct features that can significantly influence retirement income.
Defined Benefit Plans provide a guaranteed payout at retirement, often based on salary and years of service. This type of pension is typically offered by employers and can greatly reduce retiree anxiety around financial instability. Some key features include:
- Predictable income stream
- Employer takes on investment risk
- Benefits are calculated through a specific formula
Defined Contribution Plans, on the other hand, shift the responsibility of saving for retirement onto the employee. With options like 401(k) plans or IRAs, these plans allow individuals to make contributions, often matched by employers. The total pension amount at retirement depends on investment performance over the years. Pivotal aspects to consider include:
- Flexibility in contribution amounts
- Investment risk taken by the individual
- Potential for growth through market gains
Lastly, State Pensions are provided by the government and serve as a foundational income source for retirees. Eligibility usually requires a minimum period of national insurance contributions. The amount received can significantly impact the overall pension landscape for individuals. Notable points include:
- Typically less than private or employer pensions
- Inflation-linked adjustments over time
- Covers basic living needs during retirement
The Importance of Contributions and Employer Roles
Understanding the dynamics between employee contributions and employer roles is crucial for appreciating how pensions function. Employee contributions typically involve a percentage of their salary being set aside for retirement. This investment not only builds their future income but also fosters a sense of ownership and awareness about their financial wellbeing. Employees who actively engage with their contributions tend to have better retirement outcomes, as they are more likely to track their savings and make informed decisions about their investment strategies.
On the employer side, the role is multifaceted. Employers not only match employee contributions up to a certain limit but may also contribute additional funds, enhancing the overall pension pool. This matching contribution is a powerful incentive, encouraging employees to save more for their retirement. By providing robust pension plans, employers demonstrate a commitment to their workforce’s long-term financial security. This practice can enhance employee loyalty and attract talent, making it a win-win for both parties.
Moreover, employers also have a responsibility to educate their employees about the pension plan. Regular seminars, personalized reports, and financial advising can help demystify how contributions are invested and what the expected outcomes are. Such educational initiatives can empower employees to make informed choices regarding their savings strategies. The more informed an employee is, the more likely they are to make optimal decisions that maximize their retirement benefits, ultimately leading to a more secure financial future.

Maximizing Your Pension Benefits for Retirement
Understanding how to optimize your pension can have a significant impact on your financial stability during retirement. To maximize your benefits, consider employing a combination of strategies that include delaying retirement, contributing more to your pension plan, and actively engaging with financial advisors. Delaying retirement not only increases your monthly benefits but also allows your investments more time to grow, potentially boosting your overall pension value.
Additionally, regularly reviewing your pension plan can reveal options or changes that you might not be aware of. For instance, active participation in your employer’s retirement workshops can provide insight into salary deferral options or alternative investment strategies that align with your risk tolerance. Here’s a brief overview of factors to consider when evaluating your pension plan:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Retirement Age | Delaying increases monthly benefit |
| Contribution Level | Higher contributions boost final payout |
| Investment Strategy | Risk-adjusted returns can enhance growth |
Your beneficiary designations should also be periodically revisited; ensuring that your choices reflect your current intentions can lead to a smoother transfer of assets. Lastly, paying attention to tax implications when withdrawing from your pension can help you retain more of your money. By implementing these strategies, you place yourself in a stronger position to reap the full benefits of your pension during your retirement years.


Common Misconceptions About Pensions and Retirement Planning
Many people carry misconceptions about pensions that can lead to poor retirement planning. One prevalent myth is that pensions are only available to government employees or those working for large corporations. In reality, pensions can be offered by a range of employers, including non-profit organizations, educational institutions, and even small businesses. This misconception may prevent individuals from seeking out employment opportunities that offer pension plans, limiting their options for future financial security.
Another common misunderstanding is that everyone will receive a pension upon retirement. While some industries still provide pensions, many companies have shifted towards 401(k) plans or other retirement savings options. As a result, it’s crucial for individuals to take a proactive approach to their retirement planning. Understanding the type of retirement benefits available and taking personal responsibility for savings can make a significant difference in financial well-being during retirement.
Confusing the terms pension and retirement savings accounts further complicates the situation. A pension typically provides a guaranteed income based on years of service and salary, while retirement savings accounts such as a 401(k) or IRA rely on individual contributions and market performance. This distinction is vital; individuals should not rely solely on pensions and instead diversify their retirement savings strategies to ensure a stable financial future. Below is a concise comparison:
| Pension | Retirement Savings Account |
|---|---|
| Guaranteed monthly income | Dependent on individual contributions |
| Employer-funded | Employee-funded |
| Less control over investments | Greater control over investments |
| Based on salary and service years | Based on contribution and market gains |
Q&A
Q&A: Pension Explained
Q1: What is a pension?A pension is a financial plan that provides income during retirement. It’s a way for individuals to save and invest money over their working life, ensuring they have a steady cash flow when they stop working. Typically, pensions are offered by employers, governments, or private institutions, and they can be defined benefit plans (where the payout is predetermined) or defined contribution plans (where the payout depends on the contributions and investment performance).Q2: How do pensions work?Pensions work by allowing employees to contribute a portion of their salary to a retirement fund, often supplemented by employer contributions. The funds are invested over time, growing through interest, dividends, and capital gains. Upon retirement, the individual receives regular payments based on the plan’s structure and their earnings history.
Q3: What are the different types of pensions?There are primarily two types of pensions:
- Defined Benefit Plans: These plans provide a guaranteed income based on factors like salary and years of service. The employer manages the investments and assumes the financial risk.
- Defined Contribution Plans: These plans, like 401(k)s, require both the employee and employer to contribute. The retirement income depends on the total contributions plus investment performance, placing the investment risk on the employee.
Q4: Why are pensions important?Pensions are crucial for financial security in retirement. They help individuals maintain their lifestyle after leaving the workforce, covering essential expenses like housing, healthcare, and daily living costs. Without a pension, many may struggle to afford a comfortable retirement.
Q5: How can I determine how much I need to save for retirement?To determine how much you need to save, consider factors such as your desired retirement age, expected lifestyle, health expenses, and any other income sources (like social security or personal savings). A common rule of thumb is aiming for 70-80% of your pre-retirement income. Tools like retirement calculators can help project your needs based on various factors.
Q6: What happens to my pension if I change jobs?If you change jobs, your pension options will depend on the type of plan you have. For a defined benefit plan, you may be entitled to a benefit based on your years of service. For a defined contribution plan, you can often roll over your accumulated balance into a new employer’s plan or an individual retirement account (IRA) without incurring taxes.
Q7: Can I access my pension early?Accessing your pension early can be possible, but it often results in penalties and taxes. Most plans allow individuals to withdraw funds before retirement only under specific circumstances, such as financial hardship or disability. Always check with your pension plan details and regulations.
Q8: What impact does inflation have on pensions?Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your pension benefits. Some pension plans offer cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) to counteract this issue. It’s essential to consider inflation when planning for retirement, as it can significantly affect your long-term financial security.
Q9: How can I maximize my pension benefits?To maximize your pension benefits, start saving early, contribute consistently, and take advantage of employer match programs if available. Regularly review your pension options and stay informed about potential changes in regulations or benefits to ensure you’re making the most of your retirement savings.
Q10: Where can I get more information about my pension options?To learn more about your pension options, consult with your employer’s human resources department, financial advisors, or government resources that oversee retirement planning. Online tools and retirement planning seminars can also provide valuable insights.
Understanding pensions is crucial for building a secure financial future. By taking the time to educate yourself on how they work, you can make informed decisions that will benefit you in your retirement years.




0 Comments